How do they work? What are the benefits?
Introduction
Autonomous vehicles are the future. Maybe not a flying delorean, but we are seeing designs like this; back to the past to a horse and carriage style where all passengers would face each other.

On average, there are 6 million car accidents in the U.S. every year. That’s roughly 16,438 car accidents per day. Of those 6 million car accidents, over 3 million people experience a non-fatal injury and over 37,000 Americans experience death. Over 100 people die per day due to car accidents in any given year. A 2016 study by the National Highway Transportation Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that human error accounts for 96% of all auto accidents.
Could you imagine? No longer driving a car and using that time to work, read, nap or just enjoy the view on your ride? Creating a safer environment and reducing the number of car accidents, injuries and deaths. How many times were you close to hitting that biker approaching on your right that you had no idea was there? Autonomous vehicles could become a reality within the next few decades. I know it’s scary to think that a bunch of computerized vehicles are just driving around like a scene out of IRobot, but there are many positives to this scenario that could benefit the world in a major way.
What does autonomous mean?
Let’s review the definition of what an autonomous vehicle is.
An autonomous car is a vehicle capable of sensing its environment and operating without human involvement. A human passenger is not required to take control of the vehicle at any time, nor is a human passenger required to be present in the vehicle at all.
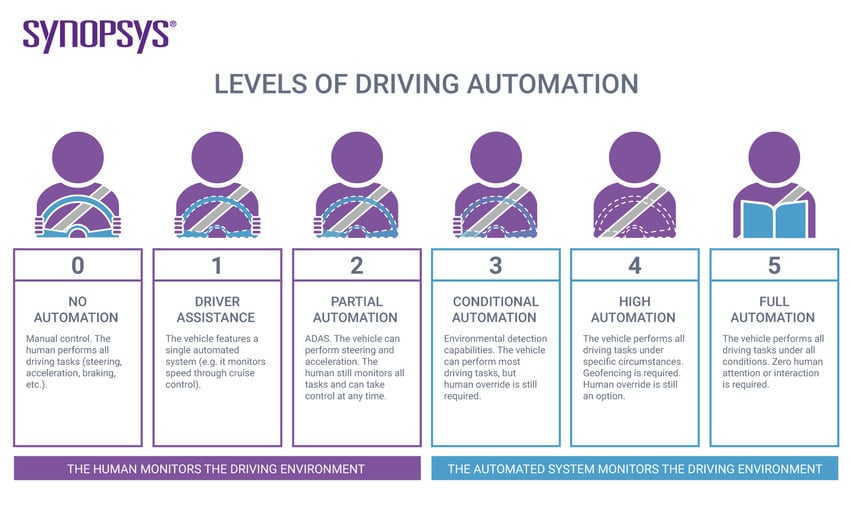
There are 6 levels of automation ranging from Level 0 (fully manual) to Level 5 (fully autonomous) which have been adopted by the U.S. Department of Transportation. Review the diagram below highlighting all levels.
How do autonomous vehicles work?
Autonomous cars rely on sensors, complex algorithms, machine learning systems, and powerful processors to execute software. Sensory input devices like cameras, radars and lidars allow a autonomous vehicle to perceive the world around it, creating a digital map.
Radio Detection and Ranging (RADAR) has been used in cars for many years and is the technology that most commonly informs adaptive cruise control and automatic emergency braking. Radar sensors monitor the position of nearby vehicles and can see objects hundreds of yards in distance and can detect their size and speeds. Radar technology cannot “see” detail and interprets images in very low resolution, meaning it can’t detect the identity of objects.
Light Imaging Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) uses laser light pulses to scan the environment, as opposed to radar’s radio waves. Lidar works by firing millions of laser signals per second, which are then reflected off object surfaces and returned to a receiver, which creates a 3D model of the car’s surroundings and measure distances, detect road edges, and identify lane markings. Lidar can see in higher resolution than radar. It’s capable of knowing whether a pedestrian is facing forwards or backward or whether a two-wheeled vehicle is a bike or a motorcycle, allowing the car’s computer to better predict how any given object will behave. It won’t work in fog or dust, which requires vehicles with lidar technology to have a secondary sensor.
Video cameras detect traffic lights, read road signs, track other vehicles, and look for pedestrians. Autonomous vehicles use camera technology to see in high resolution. A variety of lenses are placed around autonomous vehicles, providing wide-angle views of close-up surroundings and longer, narrower views of what’s ahead.
Here is an example of what each sensor “sees”:

Here’s an example of what an autonomous vehicle is processing in a given image;

Sophisticated software then processes all this sensory input, plots a path, and sends instructions to the car’s actuators, which control acceleration, braking, and steering. Hard-coded rules, obstacle avoidance algorithms, predictive modeling, and object recognition help the software follow traffic rules and navigate obstacles.
Object Recognition
Object recognition is a two-part process, object (image) classification and then object (image) localization. Object classification is determining what the objects in the image are, like a car or a person, while object localization is providing the specific location of these objects.
To perform image classification, a convolutional neural network is trained to recognize various objects, like traffic lights, cars, signs, lanes, bikes and pedestrians. A convolutional neural network performs convolution operations on images in order to classify them. To learn how to create and build a multi-label image classification CNN model, please visit my github account.
Challenges
There are many challenges in this journey to creating and releasing autonomous vehicles. Let’s highlight a few;
- Weather conditions: Rain, snow, and fog will all have a negative impact on autonomous vehicle performance
- Traffic laws and accident liability: who is liable in a car accident? Insurance companies will need to adjust as well.
- Trust: Social acceptance to this futuristic change will take time.

Benefits
- Reduce car accidents
- Reduce injuries and deaths
- Reduce traffic congestion
- Cut transportation costs (in terms of vehicles, fuel, and infrastructure)
- Free up parking lots for other uses (schools, parks, community centers)
- Reduce urban CO2 emissions
Conclusion
Autonomous cars promise to be an efficient and sustainable mode of transportation for everyone, preventing accidents, mitigating deaths, reducing C02 emissions and making commuting convenient for all. The evolution of autonomous cars is continuing and modern AI technologies and machine learning development is making rapid leaps forward. If the people’s thought hasn’t changed about autonomous vehicles being safe, the reality is these vehicles are already safe and are becoming safer. It is change that you will need to accept.